More people are increasingly looking into energy efficiency for their homes. Windows play a massive role in making your home energy-efficient from the start. That’s where U-values enter the picture.
It’s related to optimized insulation and reduced energy consumption, which helps save on heating and cooling costs. This guide breaks down U-values in simple terms, revealing how they impact your home’s efficiency.
What are U-Values for Windows?
A U-value tells you how much heat a window lets out. The lower the U-value, the better the window is at keeping warmth inside during winter. The same applies to preventing heat from entering during the summer. It’smore like a thermal barrier, as low U-values maintain a comfy indoor temperature.
In the window industry, U-values are used to rate the insulation performance of different types of glazing and frames. Manufacturers and retailers often highlight U-values to help consumers choose energy-efficient windows.When comparing some windows, it’s important to look at the U-values.
Scientifically, U-values quantify the rate of heat transfer through a material. They are expressed in watts per square meter per Kelvin (W/m²K). It means they measure how much heat passes through one square meter of a window for every degree of temperature difference between the inside and outside.
Importance of U-Values for Windows
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
Windows with low U-values minimize heat loss in winter and reduce heat gain in summer, leading to lower energy consumption. This translates to significant savings on heating and cooling costs.
Heating and cooling account for nearly 50% of a home’s energy use. Double-glazed windows typically have U-values ranging from 1.2 to3.7 W/m²K.
Meanwhile, triple-glazed windows can achieve values below 1.0 W/m²K, offering superior insulation. Homes with energy-efficient windows can reduce annual energy bills by up to 25%.
Improved Indoor Comfort
Low U-value windows help maintain a consistent indoor temperature, eliminating cold drafts and overheating issues. Key benefits include –
- Prevents cold spots near windows in winter.
- Reduces overheating in summer by limiting heat transfer.
- Enhances overall thermal comfort, making living spaces more pleasant.
Consider an office building with low U-value windows to combat temperature fluctuations. Employees report fewer complaints about cold drafts in winter and excessive heat in summer, leading to improved productivity and comfort.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Energy-efficient windows contribute to lower carbon emissions by reducing reliance on heating and cooling systems.
Buildings account for nearly 40% of global energy consumption, with windows playing a major role in heat loss. Switching to low U-value windows can reduce a home’s carbon footprint by up to 20%.
Many countries have strict building regulations that require windows to meet specific U-value standards, promoting sustainability.
Compliance with Building Regulations
Governments worldwide enforce minimum U-value standards to ensure energy efficiency in residential and commercial buildings. Some notable examples –
- UK: New homes must have windows with U-values of 1.4 W/m²K or lower.
- EU: Energy-efficient buildings require windows with U-values below 1.0 W/m²K.
- USA: ENERGY STAR-certified windows must meet strict U-value criteria based on climate zones.
For instance, a construction company ensures compliance with local building codes by installing windows with low U-values in new developments. This not only meets legal requirements but also enhances the marketability of homes as energy-efficient properties.
How Are U-Values Measured?
U-values are a key metric in determining the thermal efficiency of building materials (windows). It measures the rate of heat transfer through a material to assess insulation performance.
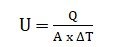
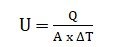
U indicates the U-value (W/m²K), Q refers to the rate of heat transfer (Watts), A is the surface area of the window (square meters), and ΔT denotes the temperature difference between the inside and outside of the window (Kelvin).
For instance, take a window with a U-value of 2.0 W/m²K. If the temperature inside is 20°C and outside is 10°C, the window will allow 2 watts of heat to escape per square meter for every degree of temperature difference.
Aside from measuring the U-value in W/m²K, you can also have it as BTU/h·ft²·F. Measure the Q in BTU/h, get the surface area (A) of the window in square feet, and the temperature difference (ΔT) should be in Fahrenheit.
1 W/m²K = 0.1762280394 BTU/h·ft²·F
1 BTU/h·ft²·F = 5.6744658974 W/m²K
U-values are calculated for the entire window (Uw). It includesU-values for the glass (Ug), the frame (Uf), and the edge of the glass (Ψg). The overall U-value (Uw) is assessed considering the areas and U-values of the glass, frame, and the thermal bridging effect at the glass edge.
Factors Affecting U-Value Measurement
- Glass Type: Low-emissivity (Low-E) coatings improve insulation.
- Gas Fill: Argon or Krypton gas between panes reduces heat transfer.
- Frame Material: Wood and composite frames have lowervalues than aluminum.
- Spacer Bars: Thermally efficient spacers minimize heat loss.
Typical U-Values for Different Window Types
U-values vary depending on the type of window and its construction. The lower the U-value, the better the window insulates against heat loss.
a. Single-Glazed Windows [TypicalValue: 5.2 – 5.8 W/m²K]
Single-glazed windows consist of a single pane of glass, offering poor insulation. They allow significant heat loss, making them inefficient for modern energy-saving standards.
b. Double-Glazed Windows [TypicalValue: 1.2 – 3.7 W/m²K]
Double-glazed windows have two panes of glass with an insulating gas (such as Argon) in between. This reduces heat transfer and improves energy efficiency. Coated double glazing can achieve even lower U-values, around 1.2 W/m²K.
c. Triple-Glazed Windows [Typical Value: 0.7 – 0.8 W/m²K]
Triple-glazed windows feature three panes of glass, offering superior insulation. They are ideal for cold climates where heat retention is crucial.
d. Vacuum Double-Glazed Windows [Typical Value: 0.7 W/m²K]
These windows use vacuum-sealed technology between two panes, significantly reducing heat transfer. They provide excellent insulation while maintaining a slim profile.
e. CU.In Glazing (Advanced Insulation) [Typical Value: 0.4 W/m²K]
CU.In glazing is an innovative window technology that achieves ultra-low U-values, making it one of the most energy-efficient options available.
Also, window frames have their U-values, which measure their thermal insulation performance. The choice of frame material has a significant impact on the overall U-value of a window.
- uPVC Frames: 1.2 – 1.4 W/m²K (Low thermal conductivity, good insulation).
- Timber Frames: 1.4 – 1.6 W/m²K (Natural insulation, slightly higher than uPVC).
- Aluminum Frames: 1.6 W/m²K or higher (Requires thermal breaks to improve insulation).
Likewise, the Uw (overall window U-value) includes both the glass (Ug) and frame (Uf).Selecting a well-insulated frame is crucial for maximizing energy efficiency.
Best U-Values for Energy-Efficient Windows
Ideal U-Value Ranges: The lower the U-value, the better the insulation. Some recommended U-values for different climates and window types –
- Single-glazed windows seem like an outdated option with poor insulation.
- Double-glazed windows offer moderate insulation, making themsuitable for mildclimates.
- Triple-glazed windows offer satisfactory insulation for cold climates.
- Vacuum double-glazed delivers high-performance insulationin colder climates.
- CU.In glazing (advanced) is suitable for ultra-energy-efficient homes.
Climate-Based Recommendations
- Cold Climates: U-values below 1.0 W/m²K are ideal for preventing heat loss.
- Moderate Climates: U-values between 1.2 – 2.5 W/m²K offer balanced insulation.
- Hot Climates: U-values below 2.5 W/m²K help reduce heat gain and cooling costs.
Certifications for Energy-Efficient Windows: Certified windows ensure high performance and compliance with energy efficiency standards. Topmost certifications to look for –
ENERGY STAR (USA and Canada): It requires windows to meet climate-specific U-value criteria.
- Northern Climate: U-value ≤ 1.4 W/m²K.
- Southern Climate: U-value ≤ 2.5 W/m²K.
Passive House Certification (Global): It requires U-values below 0.8 W/m²K for extreme energy efficiency.
- Ideal for net-zero and passive homes.
UK Building Regulations (Part L)
- New homes must have windows with U-values ≤ 1.4 W/m²K.
- Replacement windows in existing homes must meet ≤ 1.6 W/m²K.
European Energy Label (EU): It classifies windows based on U-values and solar heat gain.
- A++ rating requires U-values ≤ 0.8 W/m²K.
NFRC Certification (USA): It provides detailed window performance ratings, including U-values.
- Helps consumers compare energy-efficient options.
How to Improve Your Windows’ U-Value?
A. Upgrade to Double or Triple Glazing
Single-glazed windows have high U-values (typically 5.2–5.8 W/m²K), meaning they allow significant heat loss. Upgrading to double-glazed (1.2–3.7 W/m²K) or triple-glazed (0.7–0.8 W/m²K) windows significantly improves insulation.
- Double glazing consists of two panes of glass with an insulating gas layer in between.
- Triple glazing adds a third pane, further reducing heat transfer.
Such an upgrade comes with the following benefits –
- Reduced heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer.
- Improved indoor comfort by minimizing temperature fluctuations.
- Lowered energy bills by reducing heating and cooling needs.
B. Use Low-E (Low-Emissivity) Glass
Low-E coatings reflect heat while allowing natural light to pass through. This technology improves insulation without compromising visibility.
- Low-E coatings reduce infrared heat transfer, keeping interiors warmer in winter and cooler in summer.
- Different types of Low-E coatings are available for various climates.
Switching to a specified glass type enables –
- Enhanced energy efficiency without darkening rooms.
- Reduced UV exposure, preventing furniture fading.
- Well,working with double and triple glazing for maximum insulation.
C. Install Gas-Filled Windows
Replacing air between glass panes with argon or krypton gas improves insulation.
- Argon gas is commonly used in double-glazed windows.
- Krypton gas provides superior insulation for triple-glazed windows.
Spending on such window installation can incorporate –
- Reduced heat transfer between panes.
- Improved overall window U-value.
- Low-E coatings for maximum efficiency.
Upgrade Window Frames
The frame material has a significant impact on the overall U-value of a window. The best frame materials for low U-values –
- uPVC Frames: 1.2 – 1.4 W/m²K (Excellent insulation).
- Aluminum Frames: 1.6 W/m²K or higher (Requires thermal breaks).
- Timber Frames: 1.4 – 1.6 W/m²K (Natural insulation).
You can enjoy some distinctive advantages like –
- Reduced heat loss through window edges.
- Enhanced durability and energy efficiency.
- Direct combination with insulated glazing.
D. Improve Window Seals and Spacer Bars
Poorly sealed windows allow air leaks, reducing insulation efficiency.
- Use high-quality weatherstripping to prevent drafts.
- Upgrade to thermally efficient spacer bars to minimize heat loss.
Such measures come with the following benefits –
- Prevents air leakage and condensation.
- Enhances overall window performance.
- Works well with gas-filled and Low-E windows.
U-Value vs R-Value: What’s the Difference?
What Is R-Value?
R-value (thermal resistance) measures how well a material resists heat flow. It is expressed in square meters Kelvin per watt (m²K/W) or ft²·F·hr/BTU.
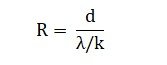
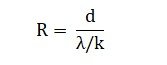
Here, d is thickness in meters/feet and is thermal conductivity in W/m·K (metric). Instead of λ, k represents the imperial unit that is measured as BTU·in/h·ft²·F.
- Higher R-values indicate better insulation.
- Used to measure insulation materials like fiberglass, foam, and walls.
- Focuses only on conductive heat transfer.
A window with an R-value of 5.0 m²K/W provides better insulation than a window with an R-value of 2.0 m²K/W, reducing heat loss.
Relationship Between U-Value and R-Value
- U-value and R-value are mathematical reciprocals. This means that lower U-values correspond to higher R-values and vice versa.
- A material with an R-value of 5.0 m²K/W has a U-value of 0.2 W/m²K. A material with an R-value of 2.0 m²K/W has a U-value of 0.5 W/m²K.
U-Value vs R-Value
| Feature | U-Value | R-Value |
| Definition | Measures heat transfer through a material | Measures resistance to heat flow |
| Unit | W/m²K | m²K/W |
| Higher Value Meaning | More heat loss (worse insulation) | Better insulation (less heat loss) |
| Lower Value Means | ||
| Used For | Windows, doors, building assemblies | Insulation materials, walls, roofs |
| Focuses On | Conductive, convective, and radiative heat transfer | Only conductive heat transfer |
| Common Range | 0.1 – 5.8 W/m²K | 1 – 50 m²K/W |
Which One Should You Use?
- For insulation materials (fiberglass, foam, walls), choose R-value.
- For windows, doors, and building assemblies, stick tothe U-value.
- For comparing energy efficiency, convert between U-value and R-value.
U-values make windows more than just transparent barriers. It actively takes part in temperature regulation, comfort, and sustainability.Select windows with low U-values to lower energy costs, improve indoor comfort, and reduce your carbon footprint.
Contact Alu Glaze aluminium window manufacturers in Birmingham for more information’s.
FAQs
Lower U-values indicate better insulation, which reduces heat loss in winter and minimizes heat gain in summer. This results in lower heating bills, improved indoor comfort, and are duced carbon footprint.
You can enhance your windows’ insulation without full replacement. Install Low-E (low-emissivity) coatings, use insulating window films, upgrade to gas-filled panes (argon or krypton), and/or improve seals and weatherstripping.



